If you work in technology or finance or invest in stocks or bonds, you must have heard of the term FinTech. We’ll see how FinTech changes the finance landscape. It is also used in conjunction with AI and Crypto-currencies to build basic financial models with Excel and more. Also, there are many use cases to explore borrowing and lending with online peer-to-peer (P2P) markets. Let’s start!
Many people mistakenly believe that financial accounting reports are simply dry, historical summaries of the past. A historical summary of a company’s past performance allows you to evaluate management performance, especially if you compare that past performance with what was planned. However, most financial management users are not interested in the past, as they are in the future. When deciding whether to loan money to a company, a banker wants to know what the company’s cash flows will be in the future. After all, it’s out of future cash flows generated by the company that the loan will be repaid. Similarly, potential investors are interested in future profits, and future cash flows. When you buy a company, you’re buying its future, not its past.
Items Itinerary to consider:
This discussion introduces you to the importance of financial models for FinTech Startups. You should not guess based on experience, rather you should be objective based on the best available information that’s out there.
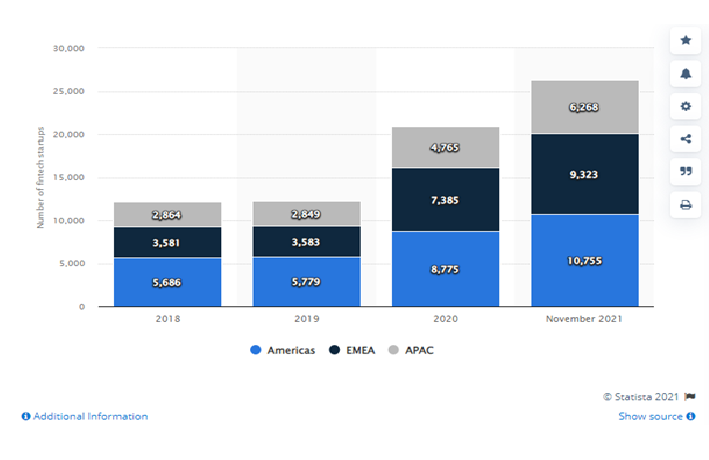
FinTech is mostly developed by start-up companies, which offer their services to established firms. It is related to the application of innovative technological solutions in the financial services industry. FinTech mostly affects mobile wallets and payments. This comes in line with an increasing number of people using a mobile banking app. Although FinTech adoption differs geographically, internet user penetration rates also play a large part, particularly mobile internet usage. Investment in FinTech is proportional to the companies offering outsized growth opportunities. FinTech related companies include:
Ideally, the aim to adopt any specific business model is to attract the right venture capital investors with FinTech experience and the right strategic investors. Following monetization models for FinTech investors can create numerous business possibilities together with personalized marketing for insurance companies. Check them out:
Without underestimating their sale cycles in both budgeting and diligence processes, start-ups must:
Know about their target audience, realistic sale cycles, the requirement of proof of concept, the need for payment for proof of concept, metrics to determine successful proof of concept, who is the decision-maker at the customer’s company, does proof of concept leads to revenue, features that lead to full commercialization, who is the ideal customer, what are the competing solutions, how much do customers pay for competing solutions, is your potential customer a good reference for a future potential customer, what is the realistic revenue ramp for this customer, do you require significant internal resources to support this customer, and are you betting your company on the right customers?
Investors in Fintech companies may want to review the company’s procedures to protect the data of employees, business partners, customers, the company’s networks, and systems. And they may need to know more about inherent cyber-security risk, administrative, technical, and operational controls to mitigate security risks, company policies, regular risk assessments, vulnerability testing, dedicated security personnel, annual risk assessment, security best practices, incident response plan, vendor risk, business continuity and disaster recovery plan, backup protocols, network monitoring, encryption, access controls, authentication, anti-virus software, and asset management, an insider threat program, privacy impact assessment, and an understanding on the reasons of past data breaches.
Fintech investors are interested in a company’s technology, and its underlying intellectual property. They are sensitive to core business revenue and expense model issues like how can they differentiate their business, what will be the customer acquisition cost, on-boarding process for new customers, can they mitigate the churn, can they detect fraud, what is their long-term value of a customer, is their service user-friendly, do they have a scalable way to acquire users, what is their ongoing product improvement cost, what level of customer support do they require, what is the ongoing product improvement cost, is the business capital intensive, can they raise sufficient capital to cover the company’s anticipated burn rate.
Lastly, investors should ensure their FinTech startup from a legal point of view, by considering if the company has been properly organized if the company is properly incorporated, contractual issues, security laws, deals/equity splits, compliance with employment laws, sexual harassment, tax considerations, employee manual, employee equity plan to incentivize employees, liability limitations, the arbitration provision in the event of a dispute, compliance with all applicable laws and regulations and potential regulatory risk.
Fintech companies either fall into the business-to-consumer sales model (B2C) or business-to-business model (B2B). Every model comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. The B2C cycle is shorter than the B2B cycle. More challenges that start-ups in the FinTech space face:
FinTech investors must keep their processes simple and budgets as lean as possible. It is always advisable to create it from the ground level, project expenses in advance, and do not overspend in the market too early. We hope that the above considerations bring some insight and relevance to FinTech App Development.
For every average and middle-class individual, their owned cars are a major expense to them. The expense does not only mean purchasing an expensive vehicle, but it is also about the recurring expenses after making the car purchase; such as repair, maintenance, fuel cost, monthly car payment, car insurance, etc. What if we tell you …
Continue reading “Best Driving Apps to Make Money in 2024”
Read More
Story Time: It’s the last of the month… and you have a low balance in your bank account. You need money to pay off an EMI, but salary payday is still two days ahead. Sounds like skating on thin ice… Right? That’s where cash advance apps like Possible Finance come into the picture. ‘Cash Advance …
Continue reading “21 Top Apps like Possible Finance to Get Instant Money in 2024”
Read More
Is the ridesharing industry saturated now? No doubt there are already a lot of best ridesharing apps globally. However, as per Statista, the leading research site, the ridesharing market is expected to grow at 22.13% annually and reach $226 billion dollars by 2028. The numbers are crazy, and to further prove our point – Arro, …
Continue reading “14 Best RideShare Apps in 2024”
Read More